Constructed wetlands
We have compiled information on constructed wetlands.
Here is an overview:
- Dimensioning of constructed wetlands
- Outflow data
- Advanced sewage treatment
- International projects
- Legal aspects
Use of constructed wetlands
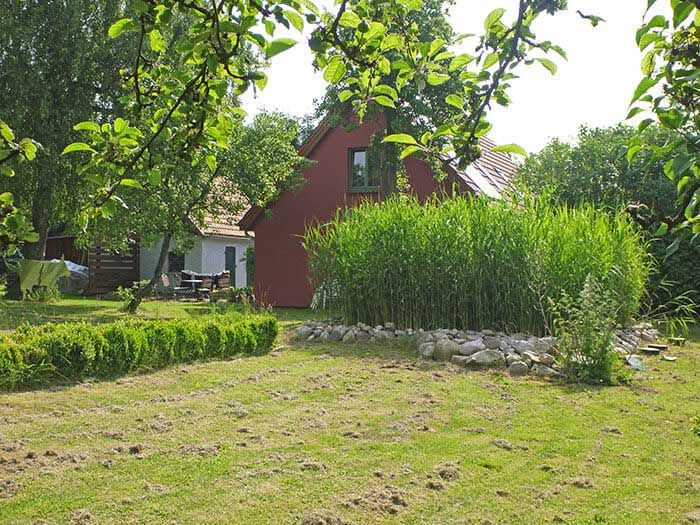
Constructed wetlands are particularly suited for the completely biological treatment of sewage from single plots, open and remote settlements where a connection to the existing sewerage system would be extremely expensive.
The scope of application of constructed wetlands is rather wide, however, not all types of sew-age may be treated in a constructed wetland. Sewage with a high sediment content, for exam-ple, must be may be pre-treated before entering the CW.
Examples for the use of constructed wetlands:
Household sewage from:
- Single plots,
- Settlements and communities of up to 1000 inhabitants.
Sharply fluctuating sewage volumes from:
- Campsites and holiday resorts,
- Cultural and sports venues not in continuous use and
- Beaches.
Rain water treatment:
- Taking rain water load off sewage pipe system
- Quasi natural rain water detention
Advantages of constructed wetlands
Constructed wetlands have the following advantages:
- Low operating costs as they produce a small amount of sludge only and do not need a lot of energy (0,- € to 3,- € per year and per 4 inhabitants),
- Maintenance by a specialist company only once a year,
- With some guidance from the planning company, customers can build the major part of the wetland themselves and thus save a lot of money,
- The parameters of the treated water are sufficiently good to reuse the water in the household (for instance for flushing the toilet),
- Due to its high volume, the system is very stable with regard to load transients,
- During the winter period, the quality parameters of the treated water deteriorate by max. 5%.
- The CW blends well with the natural surroundings and may be part of an ambitious landscape design.
Function
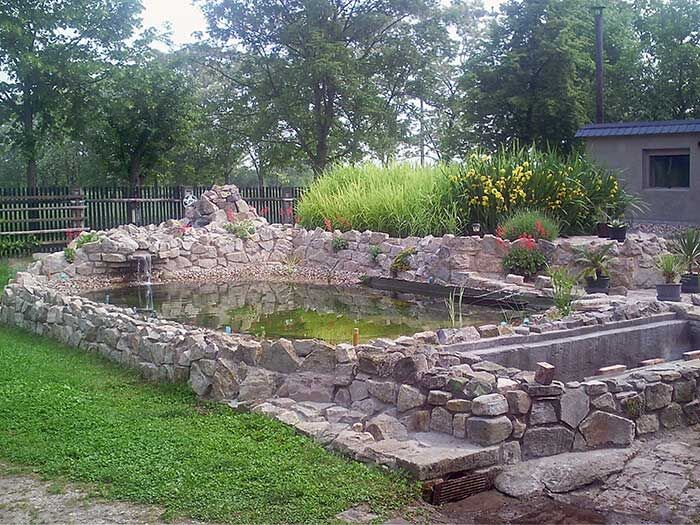
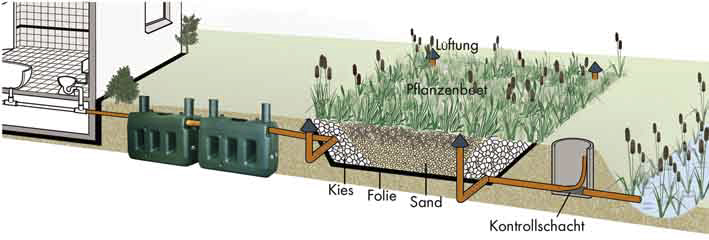
he mechanically pretreated sewage (generally coming from a multi-chamber sedimentation basin) is discharged into a basin filled with washed gravel and sand of different sizes and planted with reed, cat`s tail and irises.
The basin is sealed with a heavy-duty rubber pond liner. The roots of the plants aerate the filtering gravel and are the habitat of many bacteria which do the actual cleaning. They degrade the chemical compounds, i.e. carbon compounds, reduce nitrogen and bind phosphates.
The quality of the outflow of constructed wetlands is sufficiently good to reuse the water in the household.
Constructed wetlands: state of the art
The "state of the art" reflects the systems which have been tried and tested for a long period of time in many different places, and which can be described by a standard.
There are currently some 5,000 constructed wetlands (CW) in use in Germany, 200 of which were built for local authorities.
The sharp rise in the use of CWs, especially by local authorities for separate and com-bined sewer systems, can be attributed to the success of the standard models developed over the past few years. Consequently, sewage treatment by constructed wetlands well deserves the description state of the art.
The new DWA Worksheet A262 provides public authorities with valuable assistance when it comes to assessing planning applications.
The transition from a young pioneering technology to "state of the art" was a smooth process. Constructed wetlands have now been used for more than 30 years and have earned the appreciation of both experts and public authorities.
Constuction types
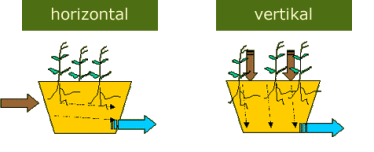
Constructed wetlands: Direction of water flow
Constructed wetlands with horizontal flow require a height difference of 1.80m from the top level of the soil against the building to the point of discharge of the treated water into a stream or the ground water.
water flow
Type of feeding
type of filter material
Dimensioning of constructed wetlands
We design and build our constructed wetlands pursuant to the ATV worksheet A 262 published by a German association of engineers in the field of sewage treatment and using our 10 years experience.
Constructed wetland with vertical flow
For the treatment of domestic sewage: 4m²/population equivalent. However, any CW must be designed for a minimum of 4 population equivalents.
Example:
Sewage from a detached house inhabited by a family with one child. The plot is level or sloping only slightly. The following is required:
- a 6m³ multi-chamber septic tank
- CW with vertical flow for 4 population equivalents x 4m² = 16m²
Constructed wetland with horizontal flow
For the treatment of domestic sewage: 5m²/population equivalent.
Example:
Sewage from a detached house inhabited by a family with one child. The plot is sloping suffi-ciently (about 2m height difference):
- a multichamber septic tank 6m³
- a constructed wetland with horizontal flow for 4 population equivalents x 5m² = 20m²
If industrial sewage is to be treated, please fill in the contact form as appropriate and we will get in contact with you.
Outflow data
As with conventional sewage treatment plants, stating the general performance of constructed wetlands is very difficult as numerous factors are involved, such as the exact design, the type of sewage to be treated and the way it is run.
However, assuming proper planning, construction and operation, the following parameters can be met:
COD - 90 mg/l
In principal it is possible to eliminate the nutrients nitrogen and phosphor completely. If you are interested in more elaborate technical solutions, do not hesitate to contact us.
Advanced sewage treatment by constructed wetlands
Potential applications
- If the treated water is discharged into a sensible receiving body,
- For sewage treatment plants in wellhead protection areas,
- If the treated water is discharged into swimming lakes,
- It the treated water is to be used for toilet flushing or watering the garden or
- If the client`s environmental standards are very high.
Possible methods
- CW with vertical flow and recirculation,
- Combination of CW with vertical and horizontal flow,
- Downstream polishing pond (additional desinfection and carbon degradation) and
- Conventional sewage treatment plus additional desinfection and carbon degradation in a CW.
Re-circulation![]()
Our CWs with vertical flow are principally designed to include sewage re-circulation. Normally this would be a manual, hydraulic re-circulation, only in cases of sharply fluctuating loads (picnic areas, campsites etc.) we use the electronic system aquatronics.
If you have any questions on advanced sewage treatment, please do not hesitate to contact us.
International projects
As our daily business and heartfelt ambition is to contribute to sustainable and cost-efficient use and treatment of water, we support the application of constructed wetlands all over the world, especially in developing countries. 20 years of professional experience and various travels into different types of communities throughout the world allow us to contribute know-how, counselling and on-site involvement in international projects. Naming a hospital in Madagascar as our pilot project, we cooperated with different organisations, mastered a variety of challenges and developed a successfully running, complex system.
Requirements & facts
- The system was to be low-cost, functional and transferable
- hospital for under-developed rural area with 150.000 inhabitants in southern Madagascar
- feasible solution for existing 30 beds as well as planned expansion
- hygienisation of drinking water from a newly dug well
- two component black water treatment system (water toilets for staff // traditional open defacation for patients & visitors)
- low-cost grey-water treatment & rainwater collection
- reuse of collected & purified water, disposal of non-reuseable water
- groundwater recharge with respect to current and future withdrawawl as well as the hydrogeological and meteorological regime
- maintanation and operation by local personnel which has to be trained on-site and, last but not least:
- the system has to match the WASH (Water, Sanitation and Hygiene) concepts in rural, clinical environments
Partners
- Wasser ohne Grenzen e.V. (WoG)
- Rotary International District 1880
- Rotary Club Ivato
- div. Rotary Clubs in Deutschland
- Network of African Academies of Sciences (NASAC)
- Elson Hanitra Madagascar Mission (EHMM)
- Doctors for Madagascar (DfM)
- Technik ohne Grenzen e.V. (TeoG)
Challenges
- rural area with limited infrastructure
- distant administration
Solutions & features
Legal aspects
Please consult the responsible authorities in your country.